Change is the only constant, and that applies well to how people search. Instead of just listing links, new AI-powered search engines and assistants are directly answering questions in conversational language. Ask ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini a question, and you often get a coherent answer without needing to click any website.
This evolution has given rise to concepts like
- Answer Engine Optimization (AEO),
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), and
- Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO).
For content creators, marketers, and brands, the challenge is clear: How do we rank and remain visible when AI is doing the searching and answering?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what AEO is, how it differs from traditional SEO and newer terms like GEO and LLMO, and how AI search engines (from ChatGPT to Google’s Gemini) retrieve and rank information.
Understanding the Evolution of Search Optimization: SEO, AEO, GEO, LLMO
How people search is transforming—and so must the way we optimize. Here’s a clear, updated primer on the key concepts driving modern search strategies.
What is SEO (Search Engine Optimization)?
SEO is the traditional practice of improving content to rank higher on search engine result pages (SERPs) like Google or Bing. It focuses on keywords, backlinks, and aligning with search algorithms to increase website traffic. The end goal: earn more organic clicks from search engines.
What is AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)?
AEO optimizes content to directly answer user queries in search results, voice assistants, or AI-powered “answer engines.” The objective is to get content featured as a concise, authoritative answer—whether as a Google snippet or a voice assistant response—rather than just a clickable link.
Key strategies include:
- Structuring content around common user questions
- Using schema markup to provide context
- Optimizing for natural language queries, especially for voice search
In short, AEO shifts focus from links to instant answers—aiming for the “position zero” that delivers what users need immediately.
What is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
GEO prepares content for AI-driven search experiences, such as Google’s Search Generative Experience or Bing Chat. These tools synthesize answers from multiple sources, so GEO ensures your content is one of them.
Core elements of GEO include:
- Publishing high-quality, trustworthy, authoritative content
- Implementing structured data for easier AI parsing
- Demonstrating strong credibility signals, aligning with Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
Think of GEO as making your content “AI-ready” for engines that generate synthesized answers, not just retrieve links.
What is LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization)?
LLMO is the practice of structuring content so large language models (LLMs)—like those powering ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude—can easily find, comprehend, and incorporate it into their responses. The aim is to make AI models familiar with your brand and content, so they mention it when users ask relevant questions.
LLMO best practices include:
- Using clear, natural language that AI can readily digest
- Ensuring your site does not block AI crawlers
- Providing factual, context-rich, and citation-worthy content
With generative AI usage surging over 1200% in late 2024, optimizing for LLMs is quickly becoming a must-have strategy.
How do AEO, GEO, and LLMO relate to each other?
These frameworks aren’t isolated silos—they overlap heavily. All three focus on making content appealing to AI-driven search experiences. The key shift from traditional SEO is where optimized content appears:
- Instead of a blue link on page one, it may now surface as a spoken answer, a featured snippet, or a chatbot response.
The core philosophy remains constant: Create content that users need and AI systems can easily interpret and trust.
Next, let’s see how these AI-based engines actually work, so we know what we’re dealing with.
How AI-Powered Search Engines Rank and Retrieve Information
AI search engines like ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and tools like Perplexity.ai don’t rely on the exact same ranking algorithms as traditional search engines—but they do follow many of the same core principles. Understanding how these systems gather and prioritize information is key to optimizing for them.
At a high level, AI-powered search follows these steps:
- Interpret the query – Understand the user’s intent.
- Retrieve relevant information – Fetch data from its knowledge base or the web.
- Generate an answer – Synthesize a response.
- Cite sources (sometimes) – Provide attribution where applicable.
Let’s break down how different AI search engines handle ranking and retrieval:
ChatGPT and Conversational AI Assistants
ChatGPT, OpenAI’s widely used AI chatbot, is powered by a large language model (currently GPT-4, with GPT-5 likely on the horizon). Initially, ChatGPT relied solely on its training data—a snapshot of internet text and other sources up to a cutoff date—meaning it could only answer based on what it had already “learned.”
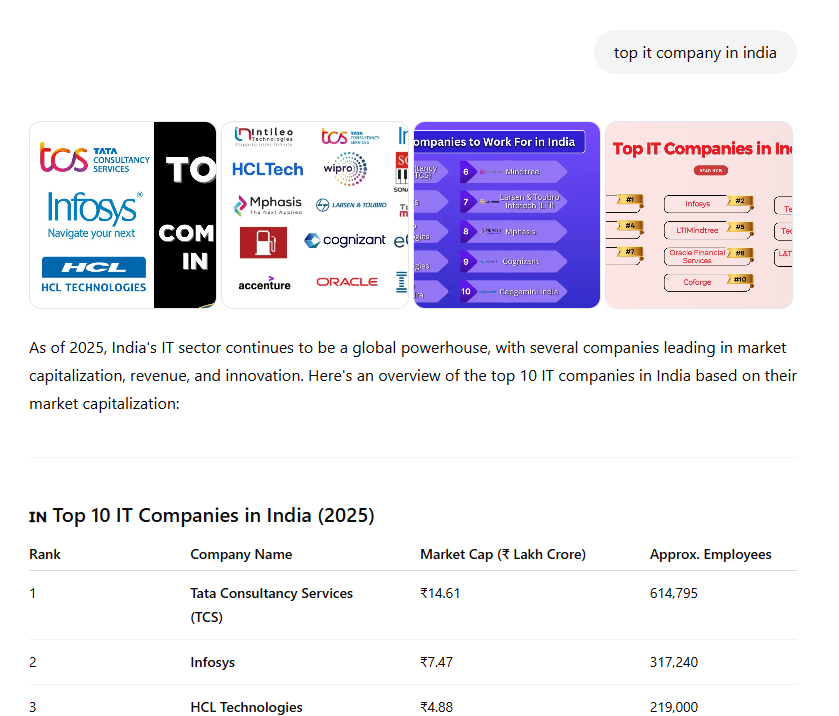
- Training Data Influence: If your content was part of the publicly available internet data scraped for training (e.g., Wikipedia, Investopedia, or well-optimized websites), ChatGPT may have absorbed it. Strong SEO and widespread content before the model’s cutoff date increase the likelihood of being included in its knowledge base.
- Live Web Browsing (2023-2025 Updates): ChatGPT now offers a browsing mode, allowing real-time web searches. In this mode, it functions like a meta-search engine: formulating queries, retrieving top results (often via Bing’s API), and synthesizing answers. Notably, it tends to prioritize top-ranking search results, meaning traditional SEO still plays a critical role in visibility.
- Citations and Brand Mentions: Unlike Bing Chat or Perplexity, ChatGPT doesn’t always cite sources directly when browsing. However, if your content is distinctive and ranks well, it may reference your brand (e.g., “According to [YourBrand]…”). High authority and frequent mentions in training data or search results increase the chances of being recommended.
Key Ranking Factors for ChatGPT & Similar AI Assistants
- Relevance & Training Data Patterns – The model favors information that aligns with patterns from its training. Widely agreed-upon facts from authoritative sources carry more weight.
- Search Engine Rankings (for Browsing Mode) – Strong SEO ensures your content appears in retrieved results.
- Content Quality & Trustworthiness – OpenAI’s browsing model may favor established sites (e.g., Wikipedia, major news outlets) while avoiding dubious sources.
- Minimal Personalization – ChatGPT doesn’t tailor answers based on user history, creating a level playing field.
Optimization Takeaway: To maximize visibility in AI search:
- Ensure your content was prominent enough to be included in training data (pre-cutoff date), or
- Maintain strong SEO rankings so AI tools pick up your content during live searches.
Google’s Generative AI Search (SGE and Gemini)
Google is integrating generative AI into search through its Search Generative Experience (SGE) and is reportedly developing Gemini, a powerful multimodal model, to enhance these capabilities. Unlike ChatGPT, which was built from scratch, Google’s AI search leverages its existing search index and ranking signals—supercharged by AI.
How Google’s AI Generates Answers
Google has indicated that its AI-generated responses in SGE synthesize information from:
- Top-ranking search results (the same pages that would appear in traditional search)
- Additional context from Knowledge Graph and other trusted databases
Research suggests that SGE combines multiple large language models (like PaLM 2 and MUM/Gemini) with Google’s core ranking systems. This means traditional SEO ranking factors—such as PageRank, Helpful Content System, and Freshness—still play a crucial role. If Google’s algorithm deems your page highly relevant and authoritative, it becomes a candidate for inclusion in the AI-generated summary.
Source Attribution & E-E-A-T
Google’s AI often cites sources indirectly, displaying website names or a “Learn more” section linking to referenced content—especially for YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics. To be featured as a source, your content must:
- Rank well in traditional search
- Meet quality thresholds (E-E-A-T—Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness is critical)
- Be verified in Google’s Knowledge Graph (e.g., having a Knowledge Panel or Wikipedia presence boosts credibility)
The Role of Freshness & Personalization
- Recency matters: Google’s Freshness algorithm influences SGE, prioritizing recent content for trending queries (even pulling from Google News and real-time updates).
- Personalization: AI search may incorporate location data (e.g., “best coffee nearby”) or user context (e.g., preferred sources for signed-in users). While speculative, Google’s history of personalized search suggests AI results could adapt to user behavior.
Bing Chat & Perplexity.ai: AI-Powered Search with Citations
Microsoft’s Bing Chat (powered by GPT-4) and Perplexity.ai represent the hybrid model of “AI + explicit citations.” These tools generate answers by querying search indexes and always cite sources, blending AI summarization with transparency. Here’s how they work—and how to optimize for them.
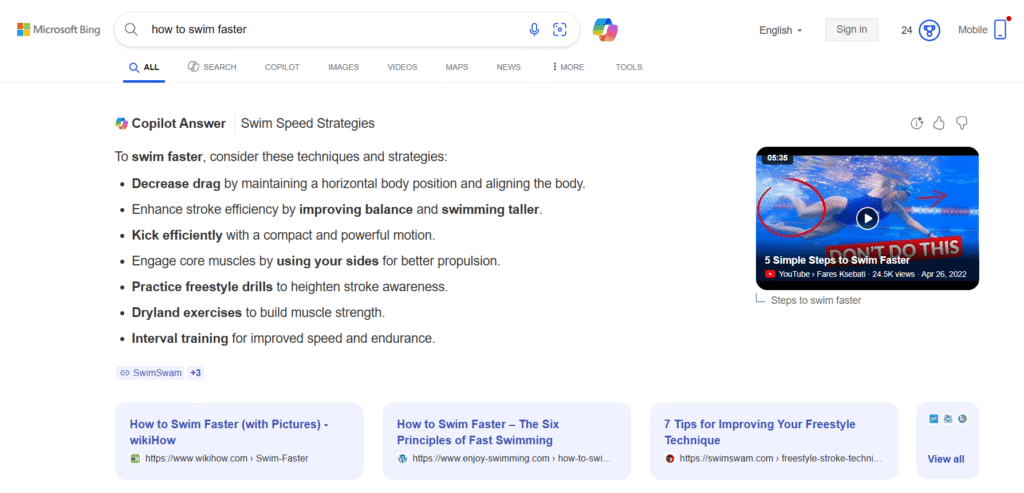
Bing Chat: AI Answers Grounded in Search Results
When you ask Bing Chat a question, it:
- Performs a Bing search and scans the top 3–5 results.
- Extracts key information—even from lower-ranked pages—if the content directly answers the query.
- Cites sources via footnotes (e.g., “[^1^]”) to maintain credibility.
Key Insights for Optimization
- Concise answers win: If your page provides a clear, succinct response, Bing’s AI may cite it even if you’re not #1.
- Authority matters: Bing prioritizes trusted sources (e.g., Wikipedia, major news outlets, Stack Overflow for tech queries).
- SEO still applies: Strong backlinks, relevance, and readability help Bing’s search (and thus its AI) discover your content.
- Avoid ambiguity: Well-structured, fact-rich content reduces AI “hallucinations” and misinterpretations.
Perplexity.ai: Research-Grade AI Search
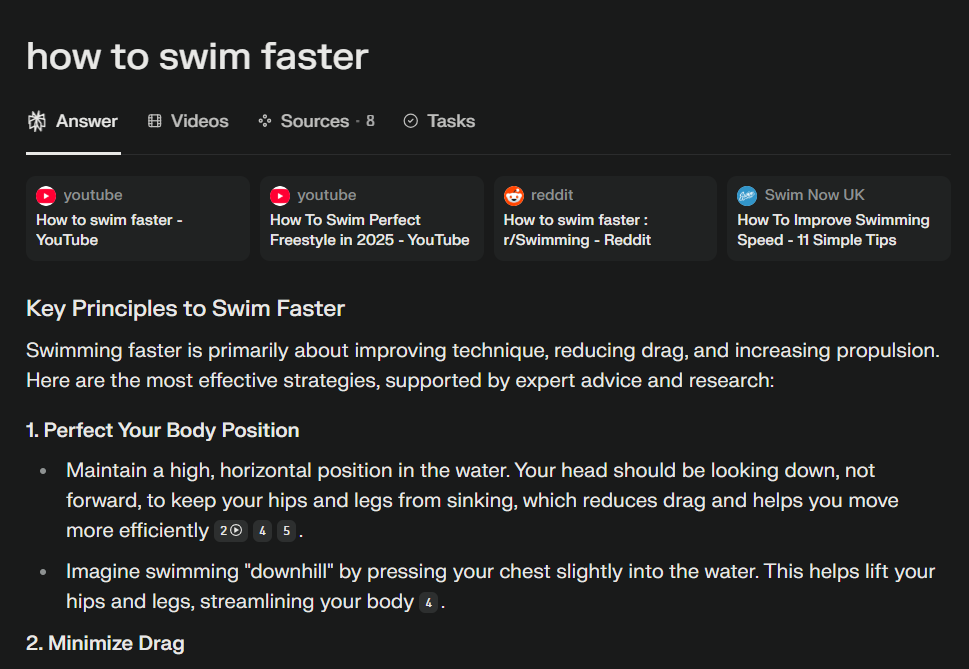
Perplexity.ai acts like a next-gen search engine, using models like GPT-4 and Claude to deliver answers with footnoted citations. It:
- Searches in real time, prioritizing authoritative sources (academic papers, government sites, niche blogs).
- Filters out low-quality content (e.g., clickbait) even if ranked highly elsewhere.
- Offers modes like “Copilot” and “Deep Research” to scan more sources for complex queries.
How to Rank in Perplexity’s Results
- Target expertise: Content from credible institutions (e.g., universities, journals) gets preference.
- Structure for clarity: Use bullet points, headers, and citations to help AI extract answers accurately.
- Prioritize freshness: Perplexity surfaces real-time updates for trending topics (e.g., live sports scores).
- Go deep: In “Deep Research” mode, comprehensive content can rank even outside the top 3.
Common Ranking Factors Across AI Search Engines
While each AI-powered search platform has unique nuances, several core ranking factors determine whether your content gets featured in AI-generated answers. Understanding these can help you optimize for visibility across Google SGE, Bing Chat, Perplexity.ai, and other emerging AI search tools.
1. Relevance to the Query
AI systems prioritize content that directly matches the user’s intent and phrasing.
- Example: A query like “how to fix a leaky faucet” will favor a page titled “5 Simple Steps to Fix a Leaky Faucet” over a generic plumbing guide.
- Optimization Tip:
- Use natural language that aligns with how users ask questions.
- Include variations of the query (e.g., “repair,” “dripping faucet”) to capture rephrased searches.
2. Authoritativeness and Trust
AI models are trained to avoid misinformation and prefer credible sources.
- Key Signals:
- Backlinks from reputable sites.
- Brand recognition (e.g., Wikipedia, established publishers).
- YMYL (Your Money Your Life) scrutiny for sensitive topics like health or finance.
- Optimization Tip:
- Build E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) into your content.
- Get cited by industry leaders or referenced in trusted databases (e.g., Knowledge Graph).
3. Clarity and Content Structure
AI parses well-organized content more efficiently.
- What Works Best:
- Clear headings (e.g., “What is [Term]?”).
- Bullet points, numbered steps, and tables.
- Concise definitions or answers near the top.
- Optimization Tip:
- Format content for easy “snippet extraction”—imagine an AI scanning for a 1–2 sentence answer.
4. Recency (Freshness)
For time-sensitive queries, up-to-date information wins.
- Example: A 2025 article on “latest electric car incentives” will outrank a 2021 version.
- Optimization Tip:
- Update old content with clear timestamps (e.g., “As of 2025…”).
- Monitor trending queries and publish quickly for breaking topics.
5. Citations and Verifiability
AI cross-checks facts against multiple sources or trusted databases.
- Key Insights:
- Content that aligns with established facts (e.g., Knowledge Graph) is favored.
- Unique data must be backed by evidence (e.g., original research with citations).
- Optimization Tip:
- Cite reputable sources within your content.
- Use schema markup to highlight key facts.
6. User Context and Personalization
AI may tailor answers based on location, language, or user history.
- Example: A query like “best coffee nearby” triggers location-aware results.
- Optimization Tip:
- Include regional specifics where relevant.
- Structure content for flexible formatting (e.g., short summaries + detailed explanations).
Now that we know what these AI engines value, let’s get into the actionable part: how to optimize your content to meet those criteria.
Optimizing Content for AI Search: Strategies and Best Practices
AI-powered search doesn’t replace traditional SEO—it enhances it. To ensure your content gets featured in AI-generated answers, you need to adapt your strategy. Below are actionable tactics to make your content more discoverable and usable by AI systems like Google SGE, Bing Chat, and Perplexity.ai.
Use Structured and Semantic Markup for Clarity
AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) and effective SEO rely on well-structured content. Logical organization helps search algorithms and AI models process information efficiently. Follow these best practices:
1. Clean HTML Structure
- Use hierarchical headings (
<h1>to<h3>) to signal content hierarchy. For example, an<h2>titled “Symptoms of Diabetes” tells AI the text beneath it lists symptoms. - Maintain uniform formatting (e.g., bold for key terms, italics for examples) to reinforce clarity, though headings are most critical.
2. Bullet Points and Lists
- Present steps, tips, or comparisons in bulleted/numbered lists. AI prioritizes these for featured snippets.
- Example: A post titled “10 Tips for Better Sleep” with each tip as a separate
<li>item is more likely to answer “How can I sleep better?” in AI-generated responses.
- Example: A post titled “10 Tips for Better Sleep” with each tip as a separate
3. Tables for Structured Data
- Use HTML tables for data-heavy content (e.g., product specs, comparisons). AI extracts precise answers (e.g., “What’s the top speed of X car?”) from structured tables.
- Tables also integrate with tools like Google’s SGE for shopping or data-rich results.
4. Schema Markup
- Implement schema.org markup to enhance search indexing and rich results. While LLMs read text, schema feeds the Knowledge Graph, which AI uses for factual verification.
- Key schemas:
FAQPage,HowTo,Article, orProduct, depending on content type. - Pro tip: Ensure
Organization/Personschemas include identifiers (e.g., Wikipedia links) to solidify entity recognition.
- Key schemas:
5. Semantic HTML5 Elements
- Use tags like
<article>,<section>, or<aside>to demarcate content. Though minor, this aids AI in skipping irrelevant sections (e.g., comments in<aside>).
Lead with Concise Answers and FAQ-Style Content
To dominate answer engines (AEO), structure your content around direct answers to user questions. Here’s how:
1. Answer-First Writing
- Immediate responses: Answer the question in the first 1–2 sentences under each heading.
- Example: For a section titled “What is Quantum Computing?”, start with:“Quantum computing leverages quantum-mechanical phenomena (e.g., superposition) to process data exponentially faster than classical computers.”
- Then elaborate: Follow the concise answer with details, examples, or context.
2. Dedicated FAQ Sections
- Standalone Q&A pairs: List common questions with brief answers (40–60 words each).
- Why it works: FAQs are prime material for voice assistants (e.g., Alexa) and AI chatbots.
- Pro tip: Use
FAQPageschema markup to boost visibility in Google’s rich results.
3. Natural Language Headings
- Frame headings as questions: Match user search intent verbatim.
- Instead of: “Benefits of Yoga”
- Use: “What Are the Benefits of Yoga?”
- Tools for research: Use AnswerThePublic or ChatGPT to identify real user queries.
4. Concise, Intent-Focused Answers
- Brevity is key: Keep core answers under 3 sentences (ideal for snippets).
- Example: For “How do I change a tire?”, lead with:“Loosen lug nuts, lift the car with a jack, swap the tire, and tighten securely.”
- Follow with details: Expand with step-by-step instructions or deeper context.
Format Content for Snippets and Citations
To maximize AI extraction and user engagement, structure your content for easy snippet generation. Follow these tactics:
1. Modular Paragraphs
- One idea per paragraph: Keep paragraphs short (1–3 sentences) and focused.
- Why it works: AI can extract standalone ideas without losing context.
- Example:“Quantum computing solves complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers by leveraging qubits.”
2. Bullet Points for Clarity
- Break down multi-part answers: Use bullets for steps, tips, or lists.
- AI advantage: Bullets are prime candidates for rich snippets and voice responses.
- Example: For “How to improve Wi-Fi signal?”:
- Reposition your router centrally.
- Reduce interference from other devices.
- Upgrade to a mesh network.
3. Contextual Facts
- Embed dates, sources, and meaning: Ensure facts are self-contained.
- Instead of: “500 million users.”
- Use: “As of 2024, Platform X has 500 million monthly active users (Statista).”
4. Neutral, Citation-Ready Tone
- Prioritize factual statements: Avoid marketing language.
- Snippet-friendly: “A 2025 Gartner study ranked Tool Y #1 for ease of use.”
- Avoid: “Our tool is the best—try it now!”
5. Third-Person Objectivity
- Remove first-person bias: Write for direct quoting.
- Instead of: “We launched Feature Z.”
- Use: “Company A launched Feature Z in June 2025.”
6. Clear Examples
- Delineate examples: Use “e.g.,” italics, or parentheses.
- Example: “Machine learning applications (e.g., fraud detection) rely on labeled datasets.”
7. Snippet-Length Optimization
Aim for 40–60 words: Break long explanations into sub-sections or lists.
Ensure Factuality, Authority, and Freshness
Quality and credibility are paramount in the AI answer world. Here’s how to make your content a trusted source for both users and algorithms:
1. Fact-Check and Cite Reliable Sources
- Verify every claim: Cross-check statistics, dates, and technical details.
- Inline citations: Embed sources naturally (e.g., “A 2025 McKinsey study found 72% of enterprises now use AI tools.”).
- Why it matters: AI prioritizes content aligned with its knowledge base. Citations act as trust signals.
2. Showcase E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
- Highlight credentials: For YMYL topics (health, finance, etc.), disclose author expertise (e.g., “Written by Dr. Jane Smith, cardiologist at Mayo Clinic”).
- Leverage trust signals: Include bylines, expert quotes, and secure site protocols (HTTPS).
- Subtle authority-building: Mention awards or legacy (e.g., “Founded in 2010, our team has been cited in The New York Times and Nature.”).
3. Prioritize Freshness
- Regular updates: Add “(Updated July 2025)” and revise outdated data.
- Timestamp key facts: “As of Q2 2025, 58% of marketers use generative AI (HubSpot).”
- Avoid “ghost updates”: Only change dates if content is substantively refreshed.
4. Depth Over Fluff
- Comprehensive coverage: Address follow-up questions and edge cases.
- AI-detects filler: Avoid keyword stuffing; focus on actionable insights.
- Example: For “How does ChatGPT work?”, explain tokenization, training data, and limitations—not just surface-level features.
5. Strengthen Organic Authority
- Earn backlinks: Collaborate with industry leaders and publish guest posts.
- Analogous to AI training: Mentions on forums/news act like “neural backlinks” for LLMs.
- Case study: Investopedia dominates finance Q&A because of its entrenched authority.
6. Lead with Data
- Concrete > vague: Replace “Many users prefer X” with “62% of users prefer X (2025 UserTesting report).”
- Structured data wins: Tables or charts boost snippet potential.
7. Polish to Perfection
- Zero-tolerance for errors: Typos confuse AI parsing and erode trust.
- Tools to use: Grammarly, Hemingway, or professional editors.
Provide Unique Insights and Original Research
Offering something unique is a powerful differentiator. AI models tend to regurgitate the common denominators of information they find. If you have original insights or data, the AI might latch onto those as novel and valuable pieces of information that others don’t provide.
1. Conduct Original Research
- Surveys, experiments, and data analysis: Generate proprietary statistics that answer unmet questions.
- Example: “Our 2025 survey of 1,200 marketers revealed 42% plan to double AI ad spend by 2026.”
- Why it works: AI prioritizes fresh, cited data. Original research also attracts backlinks (e.g., Calendly’s 2024 State of Meetings Report was cited by McKinsey).
2. Leverage Expert Voices
- Feature exclusive interviews or quotes:
- Example: *“‘Multi-factor authentication blocks 90% of targeted attacks,’ says Jane Doe, CISO at Palo Alto Networks.”*
- Credibility boost: Named experts and verifiable titles increase trust signals for AI.
3. Develop Novel Frameworks
- Introduce proprietary models or methodologies:
- Example: *“Our ‘3-Layer AI Content Filter’ identifies high-risk hallucinations in LLM outputs.”*
- Stand out: Unique frameworks avoid “vanilla” AI answers and position you as an innovator.
4. Highlight Key Findings Prominently
- Design for extraction: Use bold or standalone callouts for snackable insights.
- Example:Key Finding: “78% of users preferred simplified interfaces, driving 30% higher retention.”
- AI advantage: Clear, scannable stats are prime snippet material.
5. Amplify Through PR
- Pitch unique insights to industry media: Coverage in TechCrunch or research journals embeds your brand in AI’s knowledge base.
- Secondary citations: Even if AI cites a third party quoting you, your brand gains authority.
6. Avoid Repetitive Content
- Audit for redundancy: Ask, “Does this add something new to the conversation?”
- Synthesis as value: Combine fragmented information into actionable guides (e.g., *“The 2025 Definitive Guide to AI-Powered SEO”*).
Build Authority Beyond Your Website
One of the big themes in optimizing for AI is that it’s not just about on-page factors. It’s also about your brand’s presence across the web. AI models learn from the entire internet. So the more authoritative and present your brand/content is in various channels, the more likely an AI will view you as a trusted source. Here’s how to boost off-site signals:
1. Leverage User-Generated Content (UGC) & Communities
- Engage in forums (Reddit, Quora, Stack Overflow) where your audience seeks advice.
- Example: If users frequently recommend your product on Reddit, AI may cite those discussions in answers like “Users on Reddit praise [YourProduct] for its durability.”
- Create branded communities (e.g., a subreddit) to foster organic discussions.
- Why it works: AI trains on forum data—positive UGC acts as a “brainlink” in its knowledge base.
2. Pursue PR & Brand Mentions
- Get featured in media (Forbes, TechCrunch) or by influencers. Even unlinked mentions boost authority.
- Example: “According to Wired, [YourBrand] revolutionized X in 2025.”
- Publish press releases for milestones to seed mentions across the web.
- Data point: A Surfer study found PR efforts directly impact AI visibility.
3. Collaborate & Expand Your Footprint
- Guest posts, podcasts, and webinars position you as an industry voice.
- AI bonus: Transcripts and shared content train models to associate your brand with expertise.
- Partner with trusted entities (e.g., co-host a webinar with a top analyst firm).
4. Dominate the Knowledge Graph
- Secure a Wikipedia page (if notable) and ensure accuracy. AI heavily relies on Wiki for factual answers.
- List in industry directories (Crunchbase, G2) to strengthen entity recognition.
- Use
sameAsschema to link all brand profiles (social media, Wiki, etc.).
5. Encourage Third-Party Case Studies & Reviews
- Customer success stories on external blogs or YouTube can become direct AI citations.
- Example: “A 2025 case study by [Blog] showed [YourTool] increased ROI by 200%.”
- Monitor reviews (Trustpilot, G2) and address negatives—AI notices sentiment.
6. Track & Optimize Your AI Presence
- Use tools (e.g., Surfer’s AI Mention Tracker) to see where AI cites your brand.
- Engage with mentions: Respond to forum discussions or social media queries to reinforce visibility.
Optimize Technical Aspects for AI Discovery
While content and off-site factors are key, don’t overlook the technical side. Ensuring AI systems can access your content is foundational for everything else. Plus, new technical standards are emerging specifically for AI. Here’s what to consider:
1. Allow AI Crawlers Access
Just as you wouldn’t block Googlebot for SEO, avoid blocking AI crawlers like OpenAI’s GPTBot if you want your content included in AI answers. Opting out via robots.txt excludes your site from future AI models. Maintain a permissive robots.txt for legitimate crawlers and ensure no accidental noindex tags block indexing. While some use <!--noai--> meta tags to deter scraping, restrict these only to sensitive sections (e.g., user comments) if visibility is a priority.
2. Implement llms.txt
This emerging protocol, akin to robots.txt, provides guidelines for AI crawlers on how to use your content. Though adoption is early, it lets you specify:
- Permitted sections of your site.
- Attribution requirements (e.g., for direct excerpts).
- Licensing contact details.
Early adopters report more accurate AI responses, as clearer guidance improves content confidence for models. While not universally honored yet, proactive implementation may offer a competitive edge as major players like OpenAI and Google experiment with these standards.
3. Use AI-Specific Meta Tags
Monitor developments like Google’s indexifembedded or future tags that enable direct quoting with attribution. Adopting such features early ensures your content remains compatible with evolving AI protocols.
4. Optimize Page Speed and Reliability
AI crawlers favor fast, stable sites—just like users. Slow-loading pages risk lower rankings or timeouts during crawling (e.g., Bing’s crawler). Prioritize:
- Reliable hosting and CDNs.
- Image optimization.
- Minimal render-blocking resources.
5. Leverage Traditional Metadata
Clear title and meta description tags still matter. They influence click-through rates and help search engines—and by extension, AI—identify your page’s relevance. Even if AI answers don’t display metadata directly, well-optimized tags improve retrieval.
6. Consider Structured Data Feeds
For large-scale content producers, APIs or datasets can streamline AI ingestion. News organizations, for example, provide structured feeds to ensure proper attribution. If feasible, publish open datasets or API endpoints to make content more accessible while enforcing usage terms.
7. Monitor AI Traffic
AI tools like Bing Chat or ChatGPT’s browser may already drive traffic to your site. Track analytics for AI-specific user agents (e.g., Mozilla/5.0 (ChatGPT)) to measure impact. Google Analytics 4 can filter these referrals, revealing which content is frequently cited by AI.
Write for Humans, with AI in Mind
At the heart of every successful content strategy lies a simple truth: you’re writing for people, not machines. AI may deliver your content, but humans consume it. Google’s timeless advice—“write for people, not algorithms”—still holds, with one caveat: optimize so AI can effectively share your human-focused content.
Here’s how to strike that balance:
1. Adopt a Conversational Yet Authoritative Tone
- AI often mirrors the tone of its sources. If your content is clear and engaging (like an expert explaining to a friend), AI is more likely to preserve your phrasing.
- Avoid stiff, jargon-heavy writing—AI may oversimplify it or skip it entirely.
2. Prioritize User Intent Over Keywords
- Focus on the why behind searches. Are users seeking quick facts, step-by-step guides, or comparisons? Tailor your content to match.
- Satisfy the human need, and you’ll inherently satisfy the AI serving it.
3. Optimize for Readability
- Use short sentences, active voice, and scannable paragraphs.
- Tools like Hemingway Editor or reading aloud can help gauge natural flow.
4. Ditch Keyword Stuffing—Embrace Context
- AI understands synonyms and themes. Write naturally (e.g., “how AI ranks results” vs. forcing “AI search ranking factors” repeatedly).
- Over-optimization sounds robotic and may deter AI from quoting you.
5. Be Comprehensive (But Organized)
- Cover topics thoroughly to become a go-to source for AI. Use:
- Clear headings and subheadings.
- Tables of contents for long guides.
- Structured data (e.g., FAQs, bullet points).
6. Add Unique Value
- Ask: Does this offer something new—original insights, better examples, or deeper analysis?
- Rehashed content may rank in traditional SEO but rarely stands out in AI answers.
7. Test with AI Tools
- After publishing, ask ChatGPT or Bing Chat your target query. Analyze:
- Is your content used? If not, why?
- What makes competing answers better? Refine accordingly.
8. Avoid Manipulation—Build Trust
- Misleading tactics (e.g., fake info, content flooding) will fail as AI guardrails improve.
- Transparency (e.g., labeling AI-assisted sections) fosters credibility.
The Virtuous Cycle
- Write for humans → Engaging, high-quality content.
- Optimize for AI → Clear structure, intent alignment, and technical polish.
- Reach more humans → AI amplifies your people-first approach.
AEO, LLMO, GEO vs. Traditional SEO: Quick Comparison
To solidify the concepts, here’s a breakdown contrasting traditional SEO with Answer Engine Optimization (and its AI-focused variants like LLMO/GEO):
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) | GEO/LLMO (Generative Engine Optimization/Large Language Model Optimization) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal | Rank high on SERPs to attract clicks | Be selected as direct answer in AI-driven results (snippets, voice, chatbots) | Ensure content is recognized and cited by AI models |
| Primary Focus | Keywords, meta tags, link building | Direct question-answering, instant consumption formats | Content quality, context, and credibility for AI interpretation |
| User Interaction | User clicks a link from SERP | User gets answer directly (may not click) | Content may be synthesized by AI with/without attribution |
| Content Format | Long-form works if comprehensive | Concise, Q&A, lists, tables – answer upfront | Clearly segmented with rich context/examples |
| Ranking Signals | Backlinks, on-page SEO, CTR, speed | Schema, structured data, Knowledge Graph alignment | Brand mentions, knowledge base presence, E-E-A-T |
| Outcome Metrics | Organic traffic, rankings, conversions | Snippet count, voice answer presence | AI citation frequency, brand recall, referral traffic |
| Competition | Top 10 organic rankings | Winner-takes-most featured snippets | Quality/reputation competition across AI outputs |
| Key Differentiator | Optimize for click-throughs | Optimize for zero-click answers | Optimize for AI model recognition and trust |
The bottom line is that AEO, GEO, and LLMO are extensions, not replacements, of SEO. They represent adapting to how search is evolving. Traditional SEO tactics provide the groundwork (after all, AI systems often start with search indexes), but we need to go a step further in structuring and disseminating our content.
For businesses and content creators, the strategy should be holistic: continue excellent SEO practices and implement these AI-oriented optimizations. By doing so, you cover all your bases – whether a user clicks a search result or asks an AI assistant, they’ll find you.
Conclusion
AI-powered search isn’t coming—it’s already here. With over 25% of U.S. users now bypassing traditional search for AI tools like ChatGPT (TechRadar, 2024), the question isn’t whether to adapt, but how fast. Here’s your action plan:
1. Turn Disruption into Opportunity
- AEO/GEO/LLMO isn’t replacing SEO—it’s amplifying it.
- AI citations = machine-scale word-of-mouth. Every answer that features your content builds trust at unprecedented reach.
2. Human-Centric Content Always Wins
- AI prioritizes what helps users. Tactics like schema markup and FAQs aren’t just for algorithms—they create better experiences for people.
- Quality compounds: Optimizing for AI inherently improves traditional SEO (and vice versa).
3. Stay Ahead of the Curve
- Monitor emerging trends:
- New AI search features (e.g., Gemini’s integration).
- Evolving user behaviors (e.g., voice/multimodal queries).
- Potential “AEO guidelines” from AI providers.
- Audit regularly: Treat AI optimization like SEO—test, refine, repeat.
The Bottom Line
Ranking in AI search boils down to one rule: Be the best answer. Deliver relevant, clear, and authoritative content, and you’ll thrive—no matter how the algorithms evolve.
The future of search isn’t just something to adapt to. It’s yours to shape.