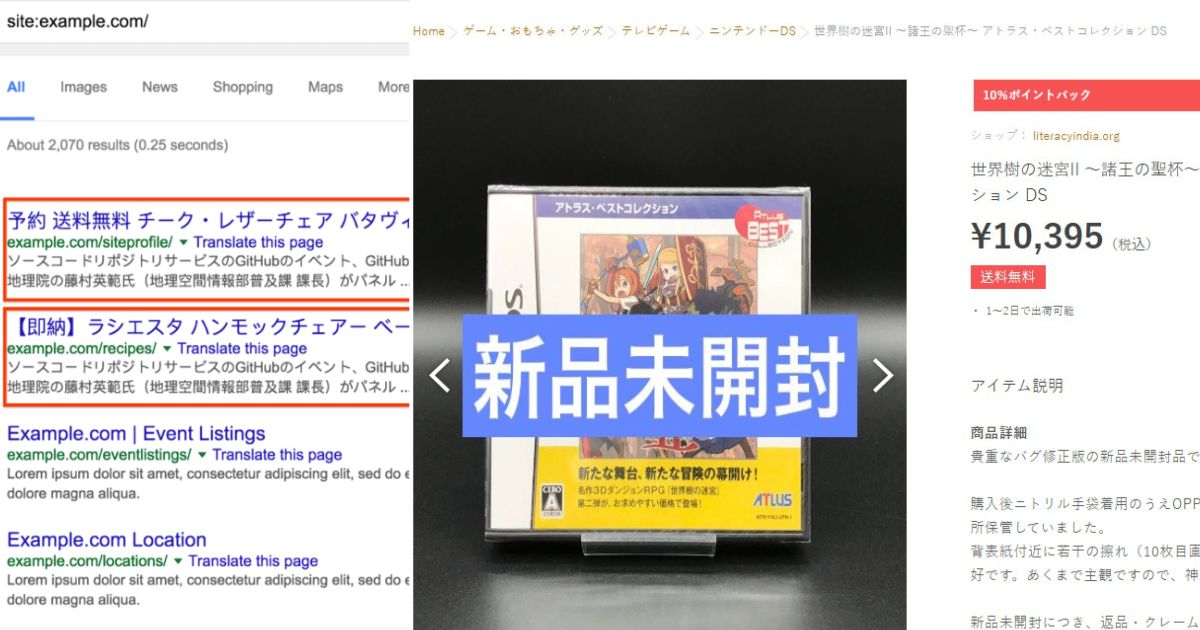
Are you seeing unusual content in a different language, such as Japanese, on your website pages? Are various Japanese pages appearing when you search for your brand or website name? If so, your website may have been infected by Japanese malware.
Don’t panic! With the right strategies, you can restore your website’s integrity and ensure it remains secure and optimized for search engines. I’ve personally helped many clients recover from similar attacks.
In this blog post, I’ll guide you through the exact steps I follow to not only clean and remove all malware from your website but also eliminate the infected Japanese results from Google Search and Google Search Console. In the end, you’ll also receive a free checklist that you can follow to seamlessly complete the process. Let’s get started.

Comprehensive SEO Cleanup and Security Checklist
1. Perform Thorough Scans with Security Plugins and Online Scanners
Why It’s Important: Identifying and isolating malware is the first step in reclaiming your website’s security. Comprehensive scans help detect hidden threats that might not be immediately visible.
How to Do It:
- Install Reputable Security Plugins: Start by installing trusted security plugins such as Wordfence, Sucuri Security, or MalCare. These plugins offer robust malware scanning, firewall protection, and real-time threat detection.
- Run a Full Scan: Use the plugin to perform a complete scan of your website. This will check all core files, themes, plugins, and the database for malicious code or suspicious activities.
- Use Online Scanners: Complement plugin scans with online tools like VirusTotal or SiteCheck by Sucuri. These tools provide an additional layer of verification by analyzing your site’s URL for known malware signatures and vulnerabilities.
- Review Scan Results: Carefully examine the scan reports. Look for flagged files, unusual code snippets, or any activities that seem out of the ordinary. Document these findings for further action.
Pro Tip: Schedule regular scans to maintain ongoing security and catch any new threats early.
2. Inspect Core Files, Themes, and Plugins for Suspicious Code or Alterations

Why It’s Important: Malware often infiltrates your site by altering core files, themes, or plugins. Detecting these changes ensures you eliminate all malicious entry points.
How to Do It:
- Access Your Files: Use an FTP client like FileZilla or your hosting provider’s file manager to access your website’s files.
- Check Core Files: Compare your core WordPress files with a fresh WordPress installation. Look for any unfamiliar or modified files, especially in the
/wp-admin/and/wp-includes/directories. - Review Themes and Plugins: Navigate to the
/wp-content/themes/and/wp-content/plugins/folders. Inspect each theme and plugin for unexpected changes or unfamiliar files. Pay attention to:- Extra PHP files that weren’t part of the original installation.
- Inline scripts or obfuscated code that appears suspicious.
- Look for Hidden Code: Search for common indicators of malware, such as
base64_decode,eval,shell_exec, orpreg_replacewith the/emodifier. These functions are often used to hide malicious scripts. - Document Alterations: Make a list of any suspicious changes or additions to address them in the cleanup process.
Pro Tip: Utilize file integrity monitoring tools provided by security plugins to automatically detect and alert you to unauthorized changes.
3. Clean Plugins and Themes
Why It’s Important: Outdated or vulnerable plugins and themes can be exploited by hackers to inject malware. Ensuring these components are clean and up-to-date minimizes security risks.
How to Do It:
- Update Everything (Make sure to have a backup of everything, if anything goes wrong you can restore): Log in to your WordPress dashboard and update all plugins and themes to their latest versions. Developers regularly release updates to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Remove Unused Plugins/Themes: Deactivate and delete any plugins or themes that are no longer in use. Even inactive components can become security liabilities if not updated.
- Reinstall from Trusted Sources: For essential plugins and themes, delete the existing versions and reinstall fresh copies from official repositories or trusted developers. This ensures that any hidden malware is removed.
- Check for Vulnerabilities: Use tools like WPScan to identify known vulnerabilities in your installed plugins and themes. Address any issues by updating or replacing affected components.
Pro Tip: Limit the number of plugins and themes to only those that are necessary and maintained regularly to reduce potential attack vectors.
4. Clean the Database of Injected Malicious Code or Entries
Why It’s Important: Malware can embed itself within your database, affecting site functionality and SEO. Cleaning the database ensures that no hidden malicious code remains.
How to Do It:
- Backup Your Database: Before making any changes, create a full backup of your database using plugins like WP-DBManager or UpdraftPlus.
- Scan for Malicious Entries: Use database optimization plugins such as WP-Optimize to scan your database for suspicious entries. Focus on critical tables like
wp_posts,wp_options, andwp_users. - Identify Unusual Data: Look for unexpected content in posts, options, or user profiles. Pay attention to:
- Suspicious scripts or iframes embedded in content.
- Unauthorized admin users or altered user roles.
- Unexpected modifications in settings that could affect site behavior.
- Remove or Sanitize Malicious Code: Carefully delete any identified malicious entries. For complex issues, consider using SQL queries to remove harmful code directly from the database.
- Optimize the Database: After cleaning, optimize the database to improve performance and remove any lingering traces of malware.
Pro Tip: Regularly clean and optimize your database to maintain site performance and reduce the risk of malware hiding within it.
5. Identify and Delete Unfamiliar or Unauthorized Files in the Website’s Root Directory
Why It’s Important: Hackers often place unauthorized files in your website’s root directory to maintain access or distribute malware. Removing these files is crucial for securing your site.
How to Do It:
- Access Root Directory: Use FTP or your hosting provider’s file manager to navigate to your website’s root directory.
- List All Files: Create a comprehensive list of all files and directories. Compare this list with a fresh WordPress installation to spot any discrepancies.
- Identify Suspicious Files: Look for files with:
- Unusual or random names (e.g.,
wp-content.php,config.bak.php). - File extensions that don’t belong (e.g.,
.php,.txt,.jpg). - Hidden files like
.hiddenfileor files with double extensions (e.g.,index.php.bak).
- Unusual or random names (e.g.,
- Delete Unauthorized Files: Carefully delete any files that you do not recognize or that appear suspicious. Ensure you have a backup before deleting to prevent accidental removal of legitimate files.
Pro Tip: Implement file permissions that restrict unauthorized file uploads and modifications to further protect your root directory.
6. Delete Backdoor Scripts or Unauthorized Access Points
Why It’s Important: Backdoor scripts enable hackers to regain access to your site even after initial vulnerabilities are patched. Removing these scripts is essential to prevent future breaches.
How to Do It:
- Search for Common Backdoors: Use FTP or file manager to search for filenames like
wp-admin.php,backdoor.php,shell.php, or other unconventional script names within your directories. - Examine Suspicious Scripts: Open and review the contents of any suspicious scripts. Look for obfuscated code, hidden functions, or unauthorized modifications.
- Remove Backdoor Scripts: Delete any identified backdoor scripts immediately. Ensure you have backups before deletion.
- Change All Passwords: After removing backdoors, change all passwords associated with your website, including:
- WordPress admin accounts
- FTP/SFTP accounts
- Hosting control panel
- Database passwords
- Update Security Keys: Update the security keys in your
wp-config.phpfile to invalidate existing sessions and enhance security. You can generate new keys using the WordPress.org Secret Key Service.
Pro Tip: Regularly monitor your files for unauthorized changes using file integrity monitoring tools provided by security plugins.
7. Audit and Delete Unauthorized User Accounts
Why It’s Important: Unauthorized user accounts can provide hackers with continuous access to your site. Auditing user accounts ensures that only trusted individuals have administrative privileges.

How to Do It:
- Access User Management: Log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Users > All Users.
- Review User List: Examine all user accounts for any unfamiliar or suspicious profiles. Pay attention to:
- Unrecognized usernames or email addresses
- Accounts with elevated privileges (e.g., Administrator role) that shouldn’t have them
- Delete Unauthorized Accounts: Carefully delete any user accounts that you did not create or recognize. Ensure you back up user data if necessary before deletion.
- Strengthen User Roles: Assign appropriate roles to remaining users, ensuring that only trusted individuals have administrative access.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement 2FA for all admin accounts to add an extra layer of security.
Pro Tip: Limit the number of admin users and regularly review user roles to maintain tight control over site access.
8. Restore the .htaccess File to Its Original State or Use a Clean Backup
Why It’s Important: The .htaccess file controls critical aspects of your website’s security and SEO. Restoring it to a clean state ensures that no malicious directives remain.
How to Do It:
- Locate the robots.txt File: Access your website’s root directory via FTP or file manager to find the
robots.txtfile. - Review Current Directives: Open the file and examine the existing rules. Ensure that it only contains legitimate directives relevant to your site’s structure.
- Remove Unauthorized Changes: Delete any suspicious or unauthorized rules that may have been added by malware. Common malicious additions might block important SEO pages or allow access to sensitive directories.
- Update Directives: Ensure your
robots.txtfile includes essential directives, such as:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /wp-includes/
Allow: /wp-content/uploads/
Sitemap: https://curiousorbit.in/sitemap.xml
- Pro Tip: Use version control systems like Git to track changes to your
.htaccessfile, making it easier to identify and revert malicious alterations. - Prevent Future Tampering: Add rules to prevent unauthorized modifications. For example, restrict access to the
robots.txtfile by adding the following to your.htaccess:
<Files robots.txt>
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from all
</Files>- Validate the File: Use tools like Google’s Robots.txt Tester to ensure your
robots.txtfile is correctly configured and free from errors. - Submit Updated robots.txt: After making changes, submit the updated
robots.txtfile to GSC to ensure search engines recognize the new directives.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and update your robots.txt file to align with your site’s evolving structure and SEO strategies.
9. Ensure Proper 404 Error Handling
Why It’s Important: Proper 404 error handling prevents search engines from indexing non-existent or malicious pages, safeguarding your SEO integrity.
How to Do It:
- Customize 404 Pages: Design a user-friendly 404 error page that guides visitors back to valid content, such as your homepage or a site map. This enhances user experience and reduces bounce rates.
- Implement Redirects: Use 301 redirects to guide users and search engines from removed or altered pages to relevant alternatives. This maintains link equity and prevents broken links.
- Prevent Indexing of 404 Pages: Ensure that your 404 pages are not indexed by search engines by adding a
noindexmeta tag:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow">- Monitor 404 Errors: Regularly check your Google Search Console’s Coverage report to identify and address any unexpected 404 errors. Fix broken links by updating or removing them as necessary.
- Pro Tip: Utilize plugins like Redirection to manage redirects efficiently and monitor 404 errors.
10. Verify Authorized Access to Google Search Console (GSC)

Why It’s Important: Maintaining control over your GSC account is essential for managing your site’s SEO and monitoring its health. Unauthorized access can lead to manipulation of your site’s SEO data.
How to Do It:
- Log in to GSC: Access your Google Search Console account associated with your website.
- Review User Permissions: Navigate to Settings > Users and Permissions to see all users with access to your GSC account.
- Remove Unauthorized Users: Identify and remove any users you do not recognize or trust. Ensure that only essential team members have access.
- Assign Appropriate Roles: Assign the correct roles (Owner, Full, or Restricted) based on each user’s responsibilities. Avoid granting unnecessary permissions.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Strengthen security by enabling 2FA for all users with access to GSC.
Pro Tip: Regularly audit your GSC user list to ensure only authorized personnel have access, especially after team changes or role updates.
11. Utilize GSC Security Issues and Manual Actions Reports

Why It’s Important: Google Search Console provides critical insights into security issues and manual penalties that can impact your site’s SEO. Addressing these reports promptly helps restore your site’s reputation and rankings.
How to Do It:
- Access Security Issues Report: In GSC, go to Security & Manual Actions > Security Issues. This report highlights detected malware, phishing attempts, or other security threats.
- Review Manual Actions: Navigate to Security & Manual Actions > Manual Actions to check if your site has received any penalties for violating Google’s guidelines.
- Follow Google’s Guidelines: For each reported issue, follow the specific instructions provided by Google to resolve it. This may involve removing malware, fixing SEO violations, or enhancing security measures.
- Request a Review: After addressing the issues, submit a review request through GSC to have the penalties lifted. Ensure all problems are thoroughly resolved before requesting a review to increase the chances of approval.
- Monitor Reports Regularly: Keep an eye on these reports to stay informed about any new security threats or penalties, allowing you to act swiftly.
Pro Tip: Set up email notifications in GSC to receive alerts about new security issues or manual actions immediately.
12. Use the URL Removal Tool in GSC for Malicious Japanese URLs

Why It’s Important: Removing malicious URLs from Google’s index is crucial for restoring your site’s reputation and preventing users from encountering harmful content.

How to Do It:
- Access the URL Removal Tool: In GSC, navigate to Removals > New Request.
- Identify Malicious URLs: Compile a list of all malicious Japanese URLs that were injected into your site during the hack.
- Submit Removal Requests: For each malicious URL, enter the complete URL into the removal tool and submit the request to delete it from Google’s search results.
- Monitor Removal Status: Track the progress of your removal requests in GSC. Ensure that all malicious URLs are successfully removed from the index.
- Prevent Re-Indexing: After removal, implement security measures to prevent these URLs from being re-indexed. This includes deleting the malicious pages and ensuring proper redirects or 404 handling.
Pro Tip: Use the bulk removal feature in GSC if you have multiple URLs to remove, saving time and effort.
13. Use the URL Inspection Tool to Request Reindexing of Cleaned Pages

Why It’s Important: After cleaning your website, requesting reindexing ensures that Google updates its index with the cleaned and optimized versions of your pages, restoring your SEO rankings.
How to Do It:
- Access the URL Inspection Tool: In GSC, go to URL Inspection and enter the URL of a cleaned page.
- Check Index Status: Verify that the page is free from errors and no longer contains malicious code.
- Request Reindexing: Click on Request Indexing to prompt Google to crawl and reindex the page. Repeat this process for all essential and cleaned pages.
- Verify Reindexing: Monitor the status of your reindexing requests in GSC to ensure that Google has successfully updated the index.
- Fix Remaining Issues: If any errors persist, address them promptly and request reindexing again until all pages are correctly indexed.
Pro Tip: Prioritize high-traffic and high-SEO value pages for reindexing to quickly recover your site’s search performance.
14. Review the Index Coverage Report
Why It’s Important: The Index Coverage report in GSC helps identify and fix any remaining indexing issues, ensuring that all your pages are correctly indexed and optimized for search engines.
How to Do It:
- Access the Index Coverage Report: In GSC, navigate to Coverage under the Index section.
- Analyze Errors and Warnings: Review any errors or warnings listed in the report, such as crawl errors, duplicate content, or blocked resources.
- Identify Problematic Pages: Locate pages that are not indexed or have indexing issues. Common problems include:
- 404 Errors: Pages that no longer exist or have been removed.
- Redirect Errors: Incorrect or broken redirects that prevent proper indexing.
- Duplicate Content: Multiple pages with similar or identical content.
- Fix Identified Issues: Address each issue based on its nature:
- 404 Errors: Redirect to relevant pages or restore the missing content if necessary.
- Redirect Errors: Correct redirect chains and ensure they point to the appropriate destinations.
- Duplicate Content: Consolidate similar pages or use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version.
- Submit Validation Requests: After fixing the issues, return to the Index Coverage report and submit validation requests to inform Google that the problems have been resolved.
- Monitor Progress: Continuously monitor the Index Coverage report to ensure all issues are addressed and that your site maintains optimal indexing health.
Pro Tip: Regularly review the Index Coverage report to proactively identify and fix new indexing issues, maintaining a healthy SEO profile.
15. Check and Update robots.txt

Why It’s Important: A well-configured robots.txt file directs search engine crawlers effectively, preventing them from accessing sensitive directories and enhancing your site’s SEO.
How to Do It:
- Locate the robots.txt File: Access your website’s root directory via FTP or file manager to find the
robots.txtfile. - Review Current Directives: Open the file and examine the existing rules. Ensure that it only contains legitimate directives relevant to your site’s structure.
- Remove Unauthorized Changes: Delete any suspicious or unauthorized rules that may have been added by malware. Common malicious additions might block important SEO pages or allow access to sensitive directories.
- Update Directives: Ensure your
robots.txtfile includes essential directives, such as:plaintextCopy codeUser-agent: * Disallow: /wp-admin/ Disallow: /wp-includes/ Allow: /wp-content/uploads/ Sitemap: https://curiousorbit.in/sitemap.xml - Prevent Future Tampering: Add rules to prevent unauthorized modifications. For example, restrict access to the
robots.txtfile by adding the following to your.htaccess:apacheCopy code<Files robots.txt> Order Allow,Deny Deny from all </Files> - Validate the File: Use tools like Google’s Robots.txt Tester to ensure your
robots.txtfile is correctly configured and free from errors. - Submit Updated robots.txt: After making changes, submit the updated
robots.txtfile to GSC to ensure search engines recognize the new directives.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and update your robots.txt file to align with your site’s evolving structure and SEO strategies.
16. Generate an Updated, Clean Sitemap
Why It’s Important: An accurate sitemap is vital for effective SEO and indexing, ensuring that search engines can crawl and index your site’s important pages without encountering malicious URLs.
How to Do It:
- Use a Sitemap Plugin: Install a plugin like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps to generate a fresh sitemap.
- Create the Sitemap: Configure the plugin to generate a sitemap that accurately reflects your current site structure. Ensure that it includes all essential pages and excludes any malicious or removed URLs.
- Exclude Malicious URLs: Double-check the sitemap to ensure no malicious URLs are included. Remove any entries that point to compromised or harmful pages.
- Submit to GSC: Go to Sitemaps in GSC and submit your updated sitemap URL (e.g.,
https://curiousorbit.in/sitemap.xml). This helps Google understand the current structure of your site and index it appropriately. - Monitor Sitemap Status: After submission, monitor the sitemap status in GSC to ensure there are no errors or warnings. Address any issues that arise promptly.
- Update Regularly: Keep your sitemap updated by regenerating it whenever you add, remove, or modify significant content on your site.
Pro Tip: Enable automatic sitemap updates in your SEO plugin to ensure your sitemap remains current without manual intervention.
17. Ensure All SEO Settings Are Correctly Configured
Why It’s Important: Proper SEO settings enhance your website’s visibility and performance, ensuring that search engines can effectively index and rank your content.
How to Do It:
- Review SEO Plugin Settings: Access your SEO plugin (e.g., Yoast SEO, All in One SEO Pack) and review all configurations. Ensure that titles, meta descriptions, and canonical tags are correctly set.
- Remove Injected SEO Elements: Check for any spammy keywords, hidden links, or unauthorized SEO manipulations introduced by malware. Remove any such elements to maintain SEO integrity.
- Optimize Titles and Descriptions: Ensure that all pages have unique and descriptive meta titles and descriptions. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally to improve search engine rankings.
- Check Canonical Tags: Verify that canonical tags are correctly implemented to prevent duplicate content issues. Each page should have a self-referencing canonical tag unless intentionally pointing to a different URL.
- Enhance On-Page SEO: Optimize on-page elements such as headings (H1, H2, etc.), image alt texts, and internal linking structures. Ensure they align with your overall SEO strategy and keyword targets.
- Validate Structured Data: If you use structured data (Schema.org), ensure it’s correctly implemented and free from errors. Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your markup.
Pro Tip: Conduct a thorough SEO audit using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify and rectify any lingering SEO issues.
18. Confirm Optimization of Meta Tags and Descriptions
Why It’s Important: Well-optimized meta tags improve click-through rates and SEO by providing clear and relevant information to search engines and users.
How to Do It:
- Access Meta Tag Settings: Use your SEO plugin to access and edit meta titles and descriptions for each page and post.
- Ensure Uniqueness: Verify that each page has a unique meta title and description. Duplicate meta tags can harm your SEO by causing confusion for search engines.
- Incorporate Targeted Keywords: Naturally include relevant keywords in your meta titles and descriptions. Avoid keyword stuffing, which can lead to penalties.
- Maintain Optimal Length: Keep meta titles under 60 characters and meta descriptions under 160 characters to ensure they display correctly in search results.
- Avoid Spammy Content: Remove any spammy or irrelevant content that may have been injected by malware. Ensure all meta tags accurately reflect the page’s content.
- Use Compelling Language: Craft meta descriptions that entice users to click by highlighting the value and relevance of your content.
- Implement Canonical Tags: Ensure canonical tags point to the preferred version of each page to prevent duplicate content issues.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and update your meta tags to align with evolving SEO trends and keyword strategies.
19. Monitor Your Website and GSC for Re-infection
Why It’s Important: Continuous monitoring helps detect and prevent future attacks, ensuring that your website remains secure and SEO-optimized.
How to Do It:
- Set Up Regular Security Scans: Schedule automated scans using your security plugins to regularly check for malware and vulnerabilities.
- Monitor GSC Alerts: Keep an eye on GSC for any new security issues or indexing problems. Address them promptly to maintain site integrity.
- Track SEO Performance: Use analytics tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor your site’s SEO performance and identify any sudden drops or anomalies.
- Review Server Logs: Regularly check your server logs for unusual activities, such as multiple failed login attempts or unexpected file changes.
- Stay Updated: Keep all website components (WordPress core, themes, plugins) updated to the latest versions to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Implement Advanced Security Measures: Consider adding additional security layers, such as Web Application Firewalls (WAF), to further protect your site from attacks.
Pro Tip: Subscribe to security newsletters and follow cybersecurity blogs to stay informed about the latest threats and protection strategies.
20. Perform Follow-Up Scans and Reviews
Why It’s Important: After the initial cleanup, ongoing reviews ensure that your website remains free from malware and maintains optimal SEO health.
How to Do It:
- Schedule Periodic Scans: Set up regular scans (weekly or monthly) using your security plugins to detect any new threats early.
- Conduct SEO Audits: Perform comprehensive SEO audits using tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to identify and fix any new SEO issues.
- Review User Activity: Monitor user accounts and permissions to ensure no unauthorized access has been granted since the last audit.
- Check File Integrity: Use file integrity monitoring tools to verify that your core files, themes, and plugins remain unchanged and free from malicious alterations.
- Update Security Measures: Continuously enhance your security protocols based on the latest best practices and emerging threats.
- Document Changes: Keep detailed records of all security and SEO-related changes to track progress and identify patterns.
Pro Tip: Create a maintenance schedule that includes both security and SEO tasks to ensure consistent site health and performance.
Download Your Free SEO Cleanup and Security Checklist Template
To help you stay organized and ensure you cover every step, download our FREE SEO Cleanup and Security Checklist for Japanese Malware Hack Excel template. This comprehensive tool will guide you through each task, making the cleanup process manageable and efficient.
Download the Free Checklist Here
Conclusion
Dealing with a Japanese malware hack can be daunting, but with a structured approach and the right tools, you can restore your website’s security and SEO performance. By following this comprehensive SEO Cleanup and Security Checklist, you not only eliminate existing threats but also fortify your site against future attacks.
Remember, maintaining a secure and optimized website is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and proactive measures. Equip yourself with the knowledge and resources to protect your digital presence, ensuring your website remains a trusted and authoritative platform in the competitive Indian market.
Stay curious, stay secure, and let your website thrive in the orbit of digital excellence.